Table of Contents
Intro: Biomedical Innovations
Biomedical Innovations Among High-Technology Industries
Forces Enabling and Constraining Internationalization
Decrease the Barriers to Internationalization
Diagram: Outline of Biomedical Innovation R&D
Technologies in biomedical innovations unite life sciences, medical sciences, data sciences, and physical sciences and aim to improve the understanding of diseases and how to diagnose and treat them.
Some examples of biomedical innovations include:
- Prosthetics
- Medical imaging solutions
- Implantable medical and drug delivery devices
- Robotic and laser instruments to assist in surgeries
- Nanomaterials
- Bioprinting
- Genome editing
Some examples of the evolving trends in biomedical innovations include:
- Personalised medicine
- Medical virtual reality
- Artificial intelligence in medical imaging
- Wearable medical devices
- Surgical robotics
- Nanorobots
- organs-on-chips
Bringing such innovations to healthcare and patient care on a global scale entails an immense amount of technical, legal and ethical considerations and requirements. Also known as the internationlisation challenge of biomedical innovations.
Biomedical Innovations Among High-Technology Industries
The industry involving biomedical innovations distinguishes itself from other high-technology industries with such fundamental dimensions as applying scientific knowledge to provide technological solutions aiming to improve health care and quality of life – in a highly regulated environment. At the same time, purchasing decisions are usually not made by end-consumers but by their physicians or such third parties as an insurance company, for example.
Early internationalisation is facilitated by simultaneous forces, both empowering and constraining operations: To recover their investments and to increase turnover, biomedical technology companies, especially, are facing a solid push towards an international outlook with high technology that has a competitive advantage at an early stage but is not culture-specific.
The first challenge that early-stage companies in the medical industry face is the need for more understanding of how the healthcare ecosystem works globally, including how to meet inherent safety design features, quality management and standardisation requirements of the diverse target markets and navigate the complex regulatory landscape.
However, finding appropriate partners is a critical challenge in internationalisation and often depends on the right network.
Forces Enabling and Constraining Internationalisation
In principle, unchanged biomedical technologies are usually introduced into international markets because manufacturers must comply with local regulations in the manufacturer’s country and assume that users will adapt to the new technology through training.
However, training is often ineffective when faced with ingrained customs and user expectations in individual countries, which can be seen during the transition phase in the increased use error rate when operating new technology.
As mentioned, the biomedical industry is highly regulated, so companies must comply with local demands in their international business activities. Logically, adhering to compliance with a single country’s requirements can result in a design likely to induce use errors in another country with different user needs and expectations or use-shaping factors.
Hence, device features should be designed cross-cultural and cross-national requirements in mind, especially as failure to meet these requirements could easily violate the international risk management (ISO 14971) and usability (IEC 62366) standard compliance.
Reimbursement strategy is another factor that most companies do not plan early enough when planning internationalisation; “Who pays for your product?” is a very relevant question as it dictates who will be financing the healthcare industry across nations. For example, in the Nordics, healthcare is mainly funded through the social security system, whereas in the US and Germany – example-wise – health insurance is the most preferred financial model.
Nonetheless, a solid push exists to expand from smaller home markets across borders due to the need to amortise high research and development (R&D) costs. Even when most companies have limited financial and managerial resources, the key challenge identified by many biomedical companies operating in an international healthcare market is to find appropriate partners for ventures.
Apart from complying with regulatory demands and financing the R&D process, organising clinical trials, including difficulties in getting access to hospitals and doctors, as well as scaling up marketing and sales, are among the challenges making an international product launch a complex endeavour.
Decrease the Barriers to Internationalisation
Companies developing biomedical innovations should prepare early on to overcome barriers in local and international markets and demonstrate credible and robust implementation measures to secure the necessary funding.
It is essential to invest in building teams of experienced medical technology, regulatory and quality control specialists to ensure the quality of the product and market access in an agile way.
It is advisable to seek input from stakeholders outside of the local ecosystem to avoid the “echo chamber” and to understand the unique added value that innovation brings to healthcare.
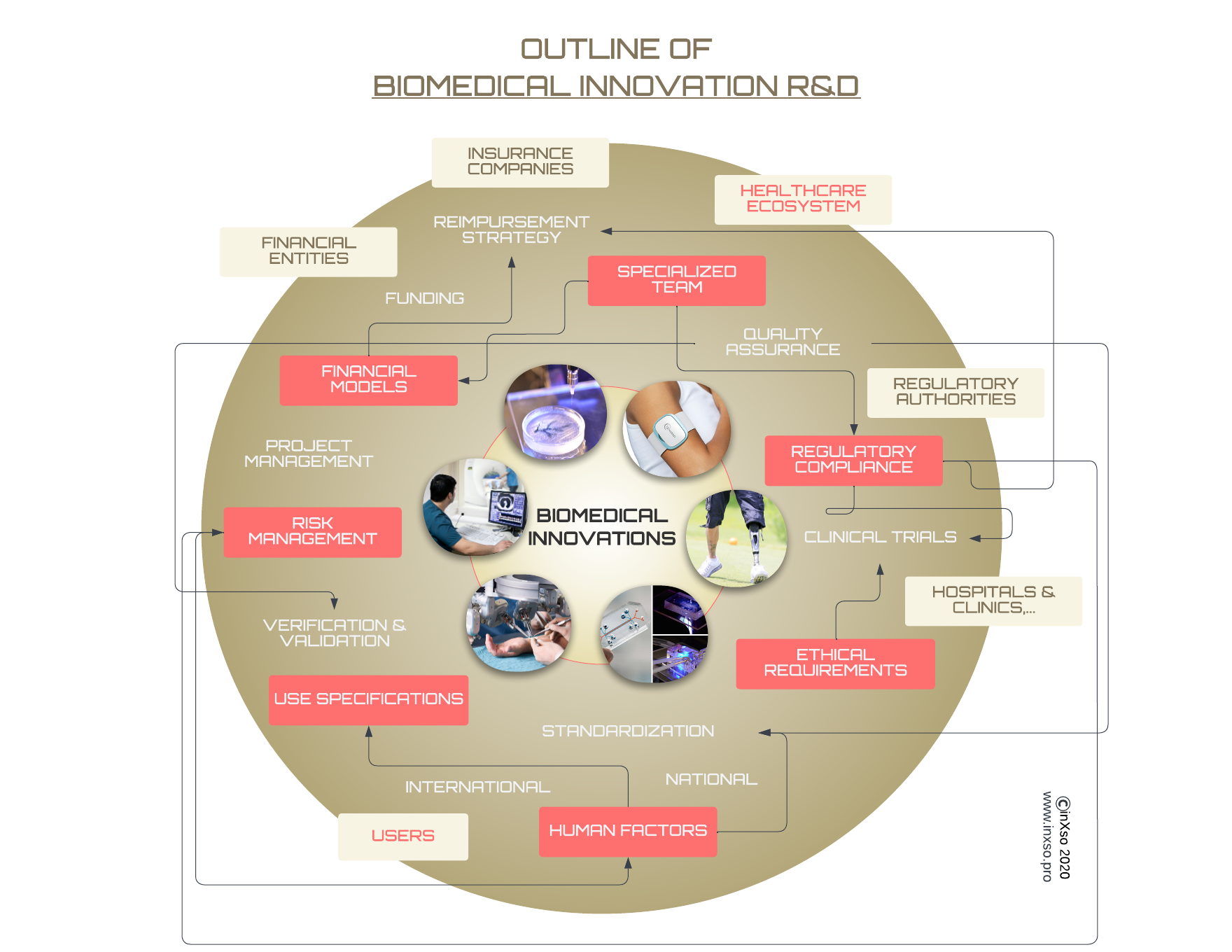
Diagram: Outline of Biomedical Innovation R&D. Non-exhaustive “mindmap” of the R&D project for Biomedical Innovation, which also constrains the internationalisation process.
